What is Fascia?
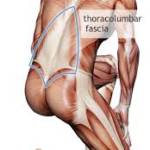
Thoracolumbar fascia
A fascia (/ˈfæʃ(i)ə/; plural fasciae /ˈfæʃii/; adjective fascial; from Latin: “band”) is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs.
The fascial network is a beautiful, crystal like, three-dimensional, spider’s web structure that is ever-flowing and uninterrupted. It encompasses the entirety of the body, connecting our superficial skin layer to the deepest tissues within us.
- Fascia connects our physicality to our physiology.
- It connects our toes to the top of our head.
- Fascia is our connective tissue.
- It can be broken down into the superficial fascia, the deep fascia and the myofascia (‘Myo’ is Latin for muscles and ‘Fascia’ for Band).
- Fascia is an elasto-collagenous matrix that is continuous. It allows us to move and be kept in posture.
- Fascia enables us to have a high degree of flexibility combined with being super, duper powerful and resilient to overstretching.
- It has a superb memory and we each have our own unique fascial fingerprint; memories and restrictions within the fascia can be stored from birth.
- It is our hydraulic shock absorber and enables the body to cope with load bearing, like gravity and mechanical stress.
- In its truest form, well hydrated and well looked after, it is fluid, dynamic to stress and powerful, allowing us to be in tip-top holistic health.
What Is Fascia Made Of?
The fascia is made up of a matrix of:
 Elastin – an elastic protein fibre that allows for stretching and contraction, it is what allows our skin to bounce back to it normal shape. It has a load-bearing role.
Elastin – an elastic protein fibre that allows for stretching and contraction, it is what allows our skin to bounce back to it normal shape. It has a load-bearing role.
Collagen – an inelastic protein fibre is the main component of our connective tissue. It has tensile properties, thus it is incredibly strong but allows a small amount of give.
Ground substance – this is a viscous gel that should be fluid and freely moving in. It has a similar character to wallpaper paste in that on impact in coagulates. When impact is traumatic (physically or emotionally) the ground substance hardens further and collagen and elastin fibres move closer together, as a result restriction occurs.
What is the role of fascia?
- The fascia encompasses and infuses every tissue in the body; our muscles, tendons, ligaments, organs, bones.
- It supports, separates and cushions all living cells in the body.
- It keeps our cells alive.
- Fascia is dynamic.
- It protects us and responds to internal and external forces, acting as our shock absorber, responsible for proprioception and stabilization; our anti-gravity system.
- It has its very own nervous, lymphatic and circulatory supply and is a communicational system for the body. It is a messenger system.
Thus, when fascia is restricted and becomes bound it has an effect on our complete health, affecting not just muscular and skeletal health. But nerve capacity, gland and organ function and our general well being.
“It is now recognised that the fascial network is one of our richest sensory organs. The surface area of this network is endowed with millions of endomysial sacs and other membranous pockets with a total surface area that by far surpasses that of the skin or any other body tissues. Interestingly, compared with muscular tissue’s innervation with muscles spindles. The fascial element of it is innervated by approximately 6 times as many sensory nerves than its red muscular counterpart.” Robert Schleip – Fascia as an organ of communication.
 What Is Fascial Restriction?
What Is Fascial Restriction?
Fascia is restricted due to various reasons, such as incorrect posture, trauma (physical and emotional), surgery, and lack of, or repetitive, movement; to name just a few.
It dehydrates, becoming a sticky matted mess of a web, shortening and hardening (Just like a muscular ‘knot’). As a consequence, extra tension is further placed on adjacent structures, such as joints, organs, and ligaments. More collagen fibres then lay down to help deal with the strain. The density of the hardened fascia increases (The ‘knot’ gets bigger).
Poor posture, constant repetitive strain and stress makes fascia not as fluid as it should be.
One restriction can lead to another.
Restricted fascia can cause aches and pains, imbalance and mind, body, and soul discomfort. Fascia restrictions come hand in hand with trapped nerves. It can also affect the efficient flow of blood and lymph, thus slowing down our bodies own healing power.
Surgery for example creates scar tissue. Scar tissue is a restriction. It acts as a rigid barrier within the fascial web, compressing nerves/blood vessels, inhibiting movement and restricting a fluid passage way. The result of scar tissue may manifest in physiological or physical dysfunction.
Myofascial release aims to restore these restrictions within the body and has been found to melt away scar tissue. The release can be quite profound. Due to the fascia’s immense memory we can hold restrictions in our body for a long time without knowing.
Restoring the fascia back to its truest and happiest from can create a huge positive shift both physical and mentally.
How Can You Keep Fascia Functioning Properly?
Good Nutrition and Hydration
Our fascia requires lots of water and a healthy, well balanced diet. Bad nutrition and not enough water will affect not only your fascia but as a consequence your musculoskeletal system. Your skin and other organ and gland functioning. So make sure you get your sufficient daily demand of joy juice.
Taking Appropriate Rest
“Rest is how the tissues rehydrate… The rhythm [of your fitness regimen] should include some rest… When you take the strain off of the tissues, like a sponge they will suck up that water and be ready for more exercise.” Tom Myers, The Anatomy Train.
Engaging in Myofascial Bodywork Treatments
Sports massage, soft/deep tissue release, and certain myofascial release techniques have been found to melt away tension within the fascia. It is never too late to energize dehydrated, hardened, sticky fascia back into its natural free and fluid form. Once the fascia is re-engaged. It has the capacity to aid our body’s own restorative nature. As a result our muscles work more efficiently.
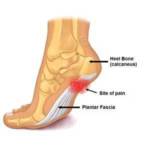
Plantar Fascia
Schedule your regular massage today to loosen up and keep your fascia healthy at book.jolitabrilliant.com
What’s a Fascia Release aka Myofascial release? Focus Neck and Back Pain
Sources:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fascia
https://www.thechirocentre.co.uk/blog/massage/fascia/#.W3jHY9hKj-Y


